Monitoring Diabetes
Not everyone with diabetes needs to monitor their blood glucose levels at home, but it is usually recommended for those using insulin, other injectable drugs, or any medication that can cause hypos. Monitoring your blood glucose levels keeps your diabetes on track and reduces the risk of developing complications. Checking can give you a better understanding of how different foods and activities impact your blood glucose levels.
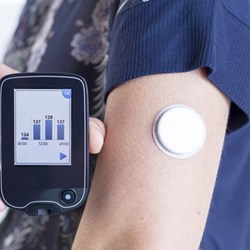
You can monitor your blood glucose levels through a finger-prick check or by using continuous glucose monitoring; either as real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) or intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring (isCGM), also known as flash glucose monitoring.
An intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitor (isCGM) / flash glucose monitor is a sensor usually worn on the arm, that records your glucose levels roughly every 5 minutes. You can scan the sensor with a reader whenever you want to.
A real-time continuous glucose monitor (rtCGM) is a device that continuously records the amount of glucose and can be inserted in the stomach area or on the arm, depending on what sort of rtCGM you have.
Both systems measure the glucose levels in the fluid just under the skin, through a small cannula which can be inserted at home and needs changing every 10-14 days. There is a time delay between the real glucose in the blood and the glucose level under the skin, so you may still need to do finger-prick tests before deciding on an insulin dose or when treating a hypo. Glucose levels change most rapidly after eating or around exercise.
Continuous glucose monitoring is offered to all people with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2 or other types of diabetes. The availability and funding for these systems will vary; so seek guidance from your local healthcare provider.
HbA1c is your average blood glucose level for the last 2-3 months. A high HbA1c result means that you have too much glucose in your blood. This is one of the diabetes care measures that you need to get at least once a year.
Have a look at the other care measures you should receive in the resource below. You can also find more resources about how you can monitor your diabetes.
Register to access your GP health results
Do you know your latest HbA1c reading? If you have diabetes you can register to access your GP diabetes health results through our patient access dashboard.
Advanced Search
Resource type -
Language -
Type of diabetes -
Carbohydrate counting is a way of matching insulin requirements with the amount of carbohydrate that you eat or drink. This course will give you everything you need to know about counting carbs.
This course provides information about continuous glucose monitoring and the Freestyle libre. It is aimed at anyone diagnosed with type 1 diabetes that is using or would like to start using a continuous glucose monitor.